Learning center
DNS concepts

DNS concepts
What is the DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a critical piece of the Internet. Its primary function is to translate human-readable names into machine-friendly addresses.

DNS concepts
What is a DNS stub resolver?
A DNS stub resolver is an operating system component that performs DNS name resolution for applications running on a computer or phone.

DNS concepts
What is a DNS zone?
A DNS zone represents a portion of the DNS namespace owned and managed as a single unit by one organization. The global DNS is composed of many zones.

DNS concepts
DNS zone delegation
Zone delegation is how a parent zone signals to DNS resolvers that authority for a child zone is served by a different set of servers.

DNS concepts
What is the DNS root zone?
The DNS is a massive tree of names containing all the names on the Internet. But it has a single starting point: the DNS root zone.

DNS concepts
Recursive vs Authoritative DNS — What's the difference?
There are two types of DNS servers: recursive and authoritative. Authoritative servers host DNS data, while recursive DNS servers perform DNS lookups for users.

DNS concepts
All DNS record types
An overview of all the DNS record types. Each DNS record type is briefly explained, and extensive explanations are available in linked articles.

DNS
DNS propagation does not exist
A widespread fallacy among IT professionals is that DNS propagates through some network. But DNS propagation does not exist.
DNS record types

DNS record types
The NS record
DNS NS records specify the authoritative name server for a domain. Learn how name server record works and how to configure them.

DNS record types
The CNAME record
DNS CNAME records are used to alias or redirect names in DNS. Learn how canonical names work in DNS, and what their restrictions are.

DNS record types
The MX record
The MX or “mail exchange” DNS record type is critical to the delivery of email via SMTP. MX records are used to specify a list of mail servers for a domain.

DNS record types
The TXT record
The TXT or “descriptive text” DNS record type was created to hold human-readable text but now plays a critical role in the prevention of spam on the Internet.

DNS record types
The A record
The A or “address” DNS record type maps DNS names to IPv4 addresses. Translating names to addresses is one of the most fundamental uses of the DNS.

DNS record types
The AAAA record
The AAAA DNS record type was created to hold IPv6 addresses. AAAA records, pronounced “quad A records” are similar to A records, but hold a 128-bit IPv6 address instead of a 32-bit IPv4 address.

DNS record types
The SOA record
DNS SOA records state that authority for a zone starts at a particular point in the tree of DNS names. Learn how they work and how they impact negative caching.

DNS record types
The SRV record
The SRV or "service locator" DNS record type enables service discovery in the DNS. SRV records allow services to be advertised on specific ports.

DNS record types
The PTR record
The PTR or "pointer" DNS record type maps an IP address to a domain name in the DNS. This is called a DNS reverse lookup.
Email and the DNS

Email and the DNS
SPF: A practical guide
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) records in the DNS identify the mail servers allowed to send email for a domain. SPF protects domains from email abuse.

Email and the DNS
DKIM: A practical guide
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) adds public key cryptography to email. Email is signed by the sender, and verified by the receiver using the DKIM record.
Email and the DNS
DMARC: A practical guide
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) is one of the three pillars of modern email security. It protects email senders and recipients from spoofing, spam, and phishing attacks.

Email and the DNS
MX vs SPF vs DMARC vs DKIM vs BIMI
Learn about the five DNS records that help control email delivery and spam prevention: MX, SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and BIMI.

Email and the DNS
How to merge DMARC records
DMARC protect domains from phishing and spam. A domain may have multiple senders for different types of email, but each domain may have only one DMARC record.

Email and the DNS
Using different DMARC records for subdomains
DMARC permits only one DMARC record per domain, but subdomains can be used when DMARC policies can't be merged.

DNS record types
The MX record
The MX or “mail exchange” DNS record type is critical to the delivery of email via SMTP. MX records are used to specify a list of mail servers for a domain.
Domain names

Domain names
How does domain name registration work?
Domain registration is the process of making a new DNS zone available on the Internet.

Domain names
10 tips for picking the perfect domain name
Your web address is as important as your brand. We've laid out 10 tips for you to pick the perfect domain name.

Holly Smith

Domain names
Finding WHOIS servers using SRV records
Every TLD registry publishes data about registered domain names using WHOIS. 36 registries publish the location of their WHOIS servers using SRV records.
Operations

Operations
The life of a DNS query in Kubernetes
In Kubernetes, DNS queries follow a specific path to resolve the IP address of a hostname. Here are all the steps and components it goes through.

Steven Reitsma

DNS
What is a good TTL for DNS?
This article will examine some of the pitfalls that come with low TTLs and will help you select appropriate TTL values.
Command line tools
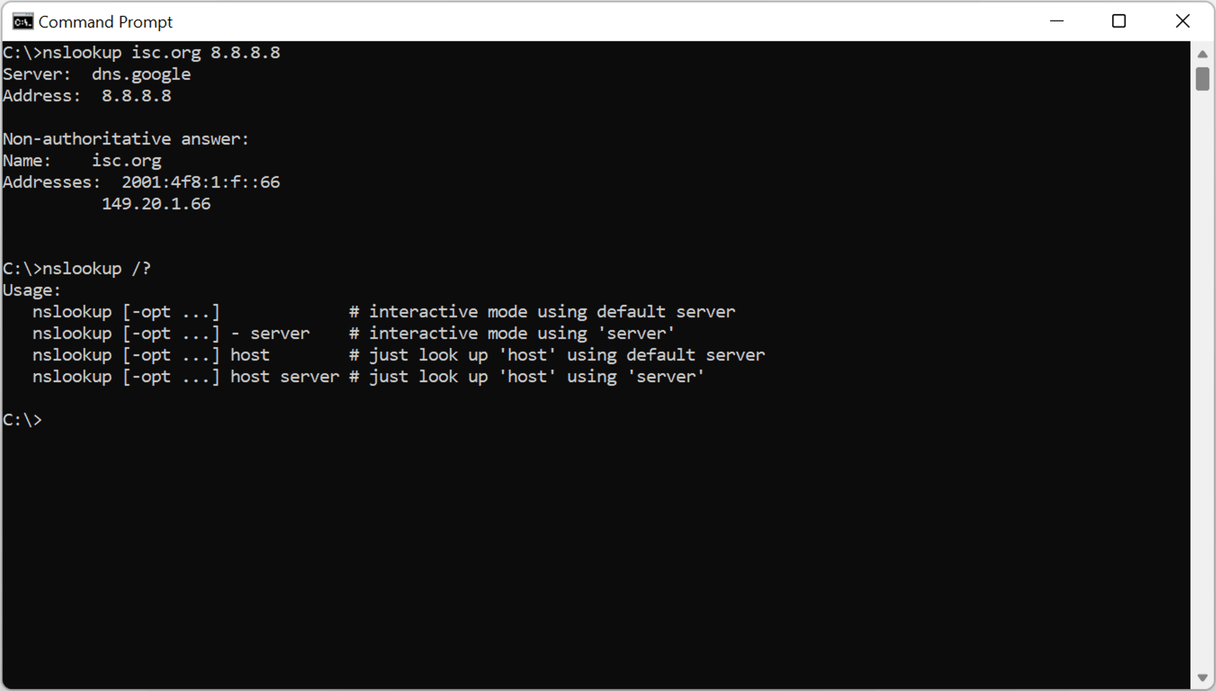
Command line tools
How to specify a DNS server in nslookup?
Nslookup uses your system's DNS server by default. You can change by specifying a DNS server in the command itself. Here's how.
Security

Security
What is the DNS Changer Malware?
The DNS changer malware changed the DNS servers of its victims. It was shut down by the FBI, Estonian police and NASA-OIG in 2011.

