All DNS record types
Copy article linkEvery DNS record has a type. This type defines what the content of the record means. For example, a DNS record of type MX contains the location of a mail exchange server. So when you want to know the mail server of some email address, you can perform a DNS lookup that queries the MX records.
A galaxy full off DNS records. By NsLookup.io. Licensed under CC By 4.0. 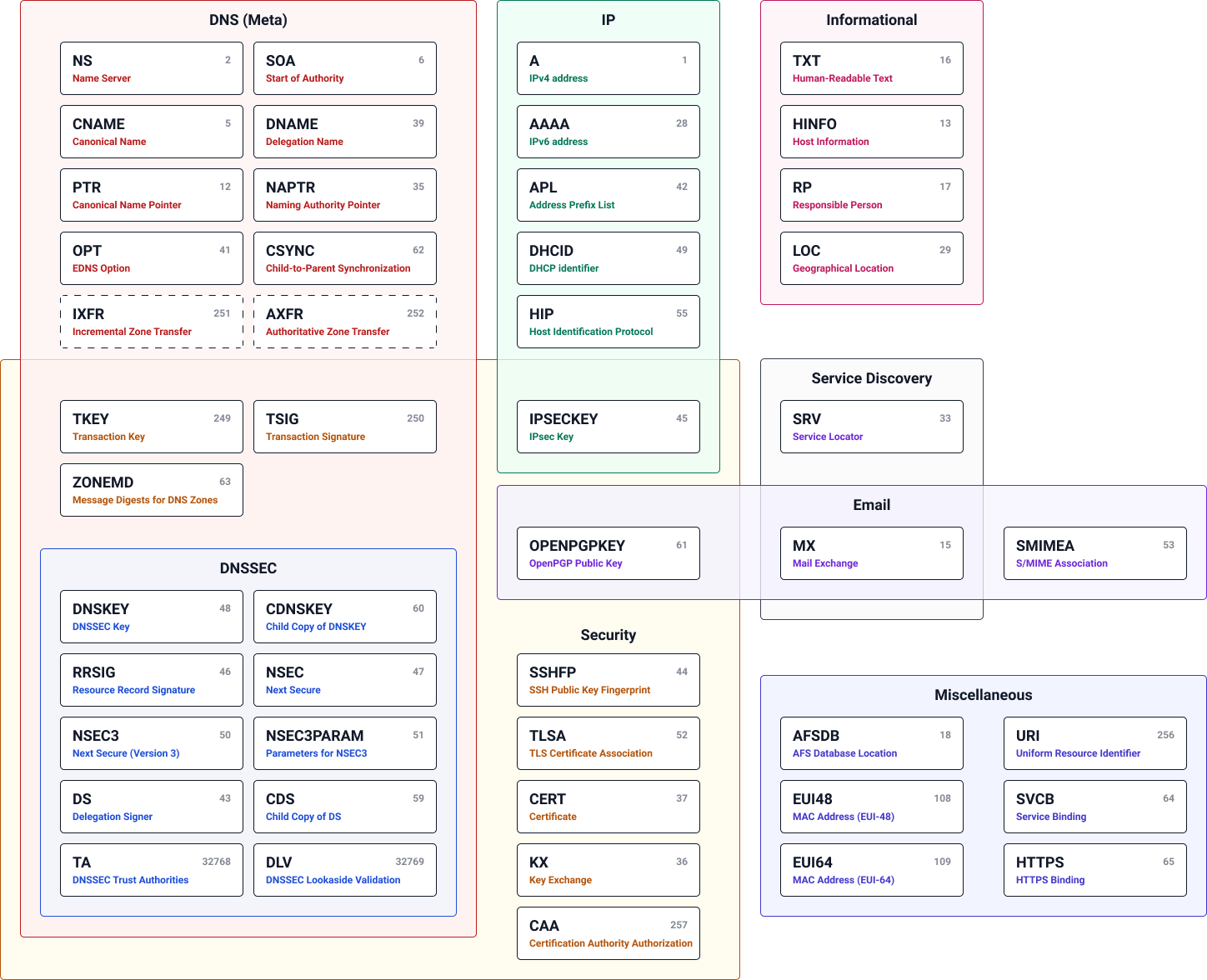
All DNS record types. By NsLookup.io. Licensed under CC By 4.0.

All the record types are strictly defined in so-called RFCs (request for comments). Since the beginning of the domain name system, a lot of new record types have been added. Some record types have also been declared obsolete, because they have been replaced by a newer record type.
There are many different types of DNS record in existence. Most of them are used only occasionally. Only a couple record types are used very frequently.

Some of the most commonly used DNS record types are:
- A — IPv4 address
- AAAA — IPv6 address
- CNAME — Canonical name
- MX — Mail exchange
- NS — Name server
- TXT — Human-readable text
- SOA — Start of authority
These are all the DNS record types that are currently in use:
- A — IPv4 address
- AAAA — IPv6 address
- AFSDB — AFS database location
- APL — Address prefix list
- AXFR — Authoritative zone transfer
- CAA — Certification authority authorization
- CDNSKEY — Child copy of a DNSKEY
- CDS — Child copy of DS
- CERT — Cryptographic certificate
- CNAME — Canonical name
- CSYNC — Child-to-parent synchronization
- DHCID — DHCP identifier
- DLV — DNSSEC lookaside validation
- DNAME — Delegation name
- DNSKEY — Cryptographic key for DNSSEC
- DS — Delegation signer
- EUI48 — MAC address (EUI-48)
- EUI64 — Mac address (EUI-64)
- HINFO — Host information
- HIP — Host identification protocol
- HTTPS — HTTPS binding
- IPSECKEY — Cryptographic key for IPsec
- IXFR — Incremental zone transfer
- KEY — Cryptographic key for DNSSEC (obsoleted by DNSKEY)
- KX — Key exchange
- LOC — Geographical location
- MX — Mail exchange
- NAPTR — Naming authority pointer
- NS — Name server
- NSEC3 — Next secure (version 3)
- NSEC3PARAM — Parameter for NSEC3
- NSEC — Next secure (obsoleted by NSEC3)
- NXT — DNSSEC key (obsoleted by NSEC)
- OPENPGPKEY — Public key for OpenPGP
- OPT — EDNS option
- PTR — Canonical name pointer
- RP — Responsible person
- RRSIG — Resource record signature for DNSSEC
- SIG — Resource record signature for DNSSEC (obsoleted by RRSIG)
- SMIMEA — S/MIME association
- SOA — Start of authority
- SSHFP — Public key fingerprint for SSH
- SVCB — Service binding
- SRV — Service locator
- TA — Trust authority for DNSSEC
- TKEY — Transaction key
- TLSA — Certificate association for TLS
- TSIG — Transaction signature
- TXT — Human-readable text
- URI — Uniform resource identifier
- ZONEMD — Message digest for DNS zones